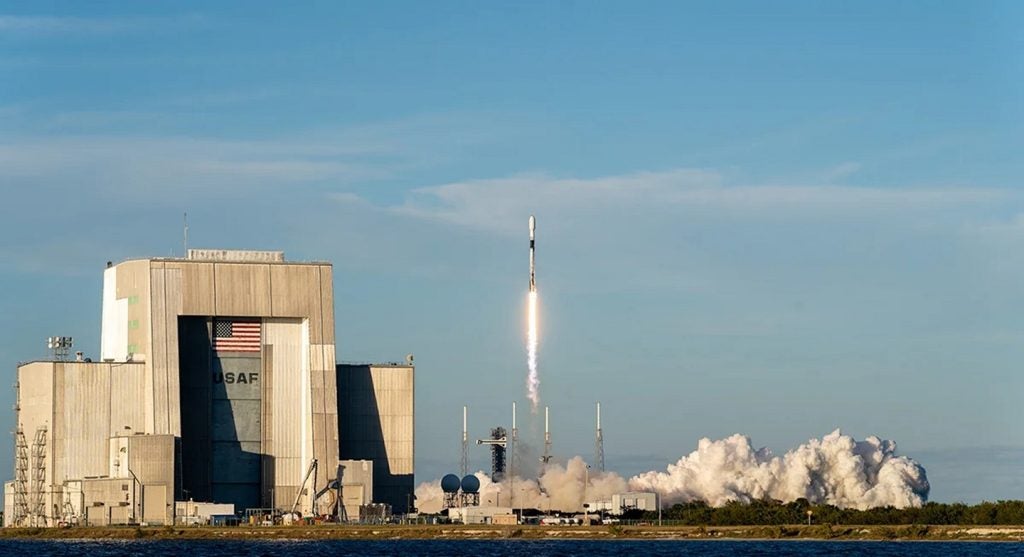
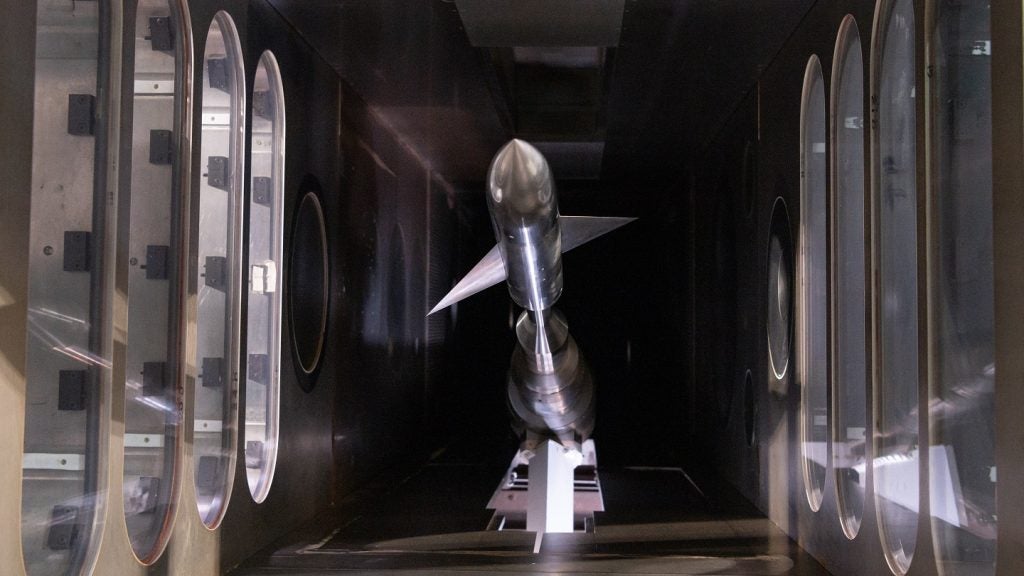
An unmanned military spacecraft, the X-37B, has been launched from Cape Canaveral US Air Force Station in Florida, US.
Powered by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne engines, the USAF craft was successfully launched using an Atlas 5 rocket.
The vehicle, which can stay in orbit for 270 days, will carry out the US space programme’s first ever autonomous re-entry and landing.
Weighing 5t, the X-37B is 9m long and just 4.5m wide, making it about a quarter of the size of the space shuttle, which is due for retirement in September.
Its power system is also different from that of the shuttle, with the X-37B using solar power and lithium-ion batteries instead of the traditional fuel cell system.
See Also:
Details of the experiments to be carried out have not been released as the USAF will be focusing on the performance of the craft during the first few flights.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalDataThe length of the mission has also not been specified, but the spaceplane is expected to land at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, US.
Development of the X-37B began in 1999 as a Nasa programme, but the project was handed over to the Pentagon in 2004.
The USAF has talked openly about the spacecraft’s design but has refused to talk about its long-term purpose.