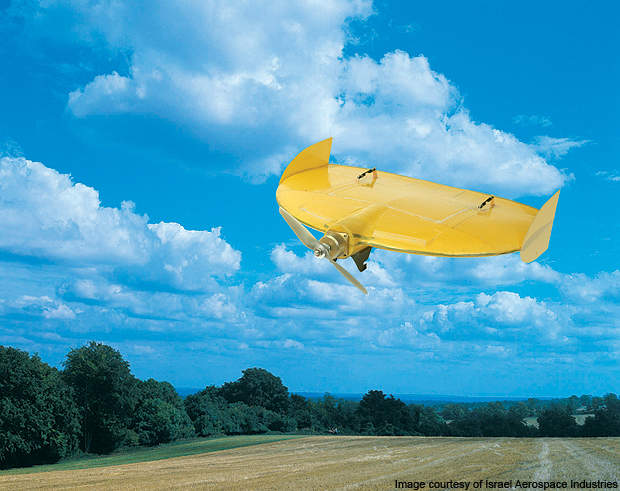
A micro unmanned aerial system (UAS), Mosquito is designed and manufactured by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for the Israel Defence Forces to perform intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations in restricted urban areas. The miniature unmanned aerial vehicle (MUAV) communicates with the ground control station through satellite communication datalink.
The maiden flight of the Mosquito was completed in January 2003. Flying at a maximum altitude of 500ft, the UAS can provide real-time imagery to operators by executing surveillance and reconnaissance missions over a small area.
The UAS is programmed to open its parachute at a desired altitude upon completion of its task wherein the operators will safely retrieve the vehicle.
Mosquito MUAV design
Mosquito is a hand or bungee-launched vehicle. It has been designed in small saucer shape. The UAV can be recovered safely upon completing its mission by landing on skids. It is designed to execute both military and commercial operations.
It was first unveiled during the design stage in 2005, and is also fitted with a compact video camera, which captures real-time imagery of the battlefield and transmits them to ground control station (GCS).
Mosquito MUAV development
Mosquito is used for technology exploration. It was first unveiled in its public demonstration flight in September 2009 at Latrun Conference. The vehicle recorded 450,000 flight hours for over 42 customers across four continents rendering a broad range of combat-proven systems.
Mosquito 1.5 is an upgraded version currently being built by IAI. It is an advanced UAS weighing around 500g.
Mosquito 1.5 UAS features advance avionics, and a partially supported high quality daylight video camera for capturing images within a range of a mile (1.6km). Its maiden flight took place in March 2004 and can loiter in air for a maximum of 60 minutes.
Features
The entire Mosquito UAS comprises a mission command and control unit, two unmanned aerial vehicles, zinc or air batteries, and communication equipment.
The Mosquito is also fitted with global positioning system (GPS) or inertial navigation system (INS) for operating the vehicle from ground control station.
Navigation
Mosquito can be controlled either manually from the ground control station or through a fully automated flight with GPS-based "in flight" way point control.
The operations can be executed using digital maps referencing and displayed on a computer screen.
Sensors
The UAS is fitted with electro-optic (EO) sensor which features a charge coupled device (CCD) camera.
The EO sensors convert light rays into electronic signals for capturing images, real-time data and videos.
IAI is also planning to deploy a daylight CCD and/or bolometric IR imager in the system in future.
Radars
Mosquito is equipped with synthetic aperture radar, maritime patrol radar, electronic support measures and a laser designator.
Ground control station (GCS)
The ground control station (GCS) is a miniature and lightweight system which displays real-time imagery or videos captured by the UAS’ payload cameras.
Processing, retrieving and monitoring of the real-time data captured by the vehicle are carried out at the GCS. Communication between the GCS and the vehicle takes place through a line of sight datalink. IAI designed and manufactured the ground control station.
Performance
Mosquito can fly at maximum altitude of 500ft. Its maximum speed is 46km/h. The range of the UAS is 3km.
It can loiter in air for a maximum of 40 minutes. The UAS weighs around 0.25kg and its maximum take-off weight is 0.5kg.